Their role as global mediating nodes of long-range communications is less prominent and respectively their mutations have a smaller effect on the ATPase activity. We argue for the functional relevance of the centrality parameters as robust indicators of functionally important sites as this network analysis captured most of the known loss-of-function mutations. The organization of the interaction networks in the studied Hsp90-cochaperone complexes gives rise to smallworld networks, marked by a relatively small number of highly connected mediators occurring mostly at the intermolecular interfaces and playing critical roles in the transmission of functional signals. Small-world networks are characterized by small separation of nodes from each other, which for proteins means a higher degree of interaction cooperativity. The vulnerability of the interaction networks to targeted perturbations of highly connected hubs may explain why mutations of these critical hot spot residues could lead to a significant loss in chaperone activity. Complex networks may be either disassortative or assortative. In the network analysis, disassortativity produces better connected but more vulnerable networks, whereas assortativity gives rise to more resilient networks. We found that the interaction networks of the Hsp90cochaperone complexes may undergo a specific rewiring of key mediating residues and assortative Saikosaponin-C growth as a result of conformational equilibrium changes during protein-protein binding. Our results also suggested that the interaction networks may evolve the network of “supporting” residues that Tenuifoliside-C acquire sufficient communication capacity to pass signal from various central mediators across the network. The evolution of various networks has been extensively studied and 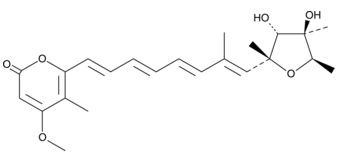 a scale-free model of network organization has gained a considerable recognition. This model is based on the idea of “preferential attachment” where the most connected nodes are more likely to acquire new edges in the course of graph evolution. The scale-free topology of a network arises from network growth and preferential attachment endowing the network with high efficiency and robustness against random errors due to a small number of central nodes and exceedingly large number of peripheral nodes. However, due to the finite size of the protein structure graphs and topological constraints, the degree distribution of protein structure networks do not follow the preferential attachment scenario and is not scale-free, but is likely to be Poissonian. The fundamental reason for deviation from the scale-free behavior is the inherently limited interacting capacity of a given residue within a structural fold due to the excluded volume effect. The scale-free networks are highly efficient in transmitting long-range signal due short paths between any pair of nodes, but could be extremely vulnerable to targeted attacks on a few key hubs that could result in splitting the global network into smaller pieces. We suggest that protein structure networks may be more tolerant to targeted attacks at the expense of some efficiency by virtue of creating broad-scale connectivity in which global hubs and central mediators are often protected by a dense network of “secondary” hubs that could mitigate the effect of targeted mutations in certain functional sites. A possible explanation for the functional lethality of some, but not all, mediating residues is that assortative hubs are likely to be responsible for long-range communications that may be compromised by deleterious mutations. Although mutations of these residues may often result in a dramatic loss of activity, some of these alterations could be rescued by the presence of wellconnected supporting hubs that may assume “responsibility for global centrality”.
a scale-free model of network organization has gained a considerable recognition. This model is based on the idea of “preferential attachment” where the most connected nodes are more likely to acquire new edges in the course of graph evolution. The scale-free topology of a network arises from network growth and preferential attachment endowing the network with high efficiency and robustness against random errors due to a small number of central nodes and exceedingly large number of peripheral nodes. However, due to the finite size of the protein structure graphs and topological constraints, the degree distribution of protein structure networks do not follow the preferential attachment scenario and is not scale-free, but is likely to be Poissonian. The fundamental reason for deviation from the scale-free behavior is the inherently limited interacting capacity of a given residue within a structural fold due to the excluded volume effect. The scale-free networks are highly efficient in transmitting long-range signal due short paths between any pair of nodes, but could be extremely vulnerable to targeted attacks on a few key hubs that could result in splitting the global network into smaller pieces. We suggest that protein structure networks may be more tolerant to targeted attacks at the expense of some efficiency by virtue of creating broad-scale connectivity in which global hubs and central mediators are often protected by a dense network of “secondary” hubs that could mitigate the effect of targeted mutations in certain functional sites. A possible explanation for the functional lethality of some, but not all, mediating residues is that assortative hubs are likely to be responsible for long-range communications that may be compromised by deleterious mutations. Although mutations of these residues may often result in a dramatic loss of activity, some of these alterations could be rescued by the presence of wellconnected supporting hubs that may assume “responsibility for global centrality”.
Author: targets inhibitor
With a high infiltrate of macrophage leukocytes in affected areas and a very low count of lymphocytes
Underpins macrophages as the first line of defense, especially in the premature gut. While the interaction between commensals and the adult gastrointestinal tract is fairly well understood, many questions remain unanswered on the acquisition of intestinal immunity during first months after birth. In our previous publications we have shown that members of Lactobacillus plantarum, strains PCS 20 and PCS 26 activate the production of reactive oxygen species, IL-6 and IFN-c in undeveloped intestinal epithelial cells as well as monocytes, orchestrating an increased anti-viral response against rotavirus, transmissible gastroenteritis virus and vesicular stomatitis virus. In conjunction with the findings of other authors that have shown individual lactobacillus strains to induce STAT1 and NF-kB shifts in adult IEC, we raise AbMole Succinylsulfathiazole several questions and concerns that have yet to be elucidated. Current available data on the interaction between LAB, IEC and gut associated lymphoid tissue is mostly based on average gene expression profiles and quantification of inflammatory products. Therefore, the question remains: what happens on the level of each individual cell and on its proteome level? In addition, virtually nothing is known about how many cells from a given population of IEC and GALT actually engage in an immunomodulatory mechanism when challenged with LAB. Further, prior studies in this direction have been performed on transformed or cancer derived cell lines like CaCo-2 and HT-29, which are known to differ from a healthy in vivo environment due to 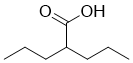 their difference in glycosylation and phenotype. Finally, the majority of studies were designed as monolayer models with the lack of associated cell types despite the need of IEC for intracellular feedback. The aim of our work was to shed more light on the mechanics of immunomodulation by specific commensal bacteria in the developing intestine and at the same time to present a reliable alternative model for gut immunology studies. By using imaging multicolor flow cytometry we have monitored the translocation of NF-kB p65 and STAT1, two of the most important intracellular orchestrators of an antimicrobial response, in untransformed polarized human neonatal small intestinal epithelia, challenged with different Lactobacillus spp. strains, and in macrophage cells that have been simultaneously co-cultured in a reductionist human 3D model of the immature gut. Imaging multicolor flow cytometry allowed us not only to monitor each individual cell but also to create a picture of how many cells from a certain population initiated cytoplasmic shifts. Additionally, we show that not only cell culture selection is important in this type of research but also the culturing technique itself. Epithelia act differently when grown on plastic surfaces than when grown on microporous membranes and need the presence of other associated cell types like macrophages and dendritic cells to show in vivo-like characteristics. The development of a normal and functioning immune system is largely dependent on the interaction of the newborn with the commensal microbiome which is one of the key players assuring intact immune homeostasis. This constant interplay between microorganisms, the gut, and associated lymphoid tissue is believed to result in a persistent stimulation, sensitation, and priming of the hosts immune system. We have shown that specific strains of Lactobacillus are able to trigger increased translocation of STAT1 and NF-kB p65 in untransformed intestinal epithelial cells and that this signal translates further into macrophages. NF-kB is a nuclear factor composed of several protein subunits regulating DNA transcription that is present in its AbMole Diperodon inactive form in the cytoplasm.
their difference in glycosylation and phenotype. Finally, the majority of studies were designed as monolayer models with the lack of associated cell types despite the need of IEC for intracellular feedback. The aim of our work was to shed more light on the mechanics of immunomodulation by specific commensal bacteria in the developing intestine and at the same time to present a reliable alternative model for gut immunology studies. By using imaging multicolor flow cytometry we have monitored the translocation of NF-kB p65 and STAT1, two of the most important intracellular orchestrators of an antimicrobial response, in untransformed polarized human neonatal small intestinal epithelia, challenged with different Lactobacillus spp. strains, and in macrophage cells that have been simultaneously co-cultured in a reductionist human 3D model of the immature gut. Imaging multicolor flow cytometry allowed us not only to monitor each individual cell but also to create a picture of how many cells from a certain population initiated cytoplasmic shifts. Additionally, we show that not only cell culture selection is important in this type of research but also the culturing technique itself. Epithelia act differently when grown on plastic surfaces than when grown on microporous membranes and need the presence of other associated cell types like macrophages and dendritic cells to show in vivo-like characteristics. The development of a normal and functioning immune system is largely dependent on the interaction of the newborn with the commensal microbiome which is one of the key players assuring intact immune homeostasis. This constant interplay between microorganisms, the gut, and associated lymphoid tissue is believed to result in a persistent stimulation, sensitation, and priming of the hosts immune system. We have shown that specific strains of Lactobacillus are able to trigger increased translocation of STAT1 and NF-kB p65 in untransformed intestinal epithelial cells and that this signal translates further into macrophages. NF-kB is a nuclear factor composed of several protein subunits regulating DNA transcription that is present in its AbMole Diperodon inactive form in the cytoplasm.
Cinnamaldehyde a major constituent of cinnamon essential oils exists naturally in the bark
Hyperglycemia is not properly managed. Marine-derived actinomycetes are rich sources of novel secondary metabolites which harbour unique structures and have diverse biological activities such as antimicrobial, antitumor and immunosuppressive activities. 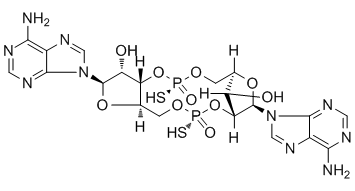 The obligate marine genera Salinispora and Marinispora have been characterized, and structurally unique and biologically active secondary metabolites have been isolated, such as salinosporamide A with excellent cytotoxicity from S. tropica CNB-392 and marinomycins A with strong antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities from Marinispora sp. CNQ-140. Marine-derived streptomycetes are also widely studied as novel antibiotic producers, where interesting compounds with antibacterial activities and anticancer activities were reported to be isolated. In our previous studies, a marine-derived actinobacterium Streptomyces xinghaiensis was identified to be a new species, which was proved to exhibit broad-spectrum antibacterial activities. However, so far no AbMole (R)-(-)-Modafinic acid sulfoxide antibiotic has been reported to be produced by microorganisms. The sulfoxide moiety presented in xinghaiamine A is unprecedented in metabolites from marine actinomycete. Sulfoxide compounds have broadspectrum of biological activities, including excellent antimicrobial, pesticidic and antitumor activities, and chemical synthesis of sulfoxide compounds also has aroused the interests of researchers. The isolation of xinghaiamine A seems to provide powerful potential to combat the emergence of multi-drugresistant microbial pathogens. In addition, compared with cisplatin, xinghaiamine A also displayed promising cytotoxic activities against a series of human cancer cell lines. Recently, the rapid development of resistance to multiple drugs in tumor chemotherapy has urged for the searching for novel drugs and the results above revealed that xinghaiamine A could be a potential clinically useful antitumor drug to combat with the increasing multi-drug resistant cancer cell lines, and the current study provided basis for further develop this novel compound for anticancer therapy. The oomycete Phytophthora capsici is a destructive fungus-like plant pathogen, which infects solanaceous and cucurbitaceous hosts including snap, lima, cucumber, eggplant, tomato, pepper, pumpkin, squash, melon, and zucchini. P. capsici has both a sexual and asexual life of cycle. Plants infected with P. capsici show various disease symptoms, such as foliar blights, fruit rots, stem and root rots. The preventive and frequent application of fungicides can limit disease expanding, but the increasing resistance of P. capsici to fungicides such as mefenoxam and pyrimorph, has been widely documented in some vegetable production regions. New fungicides aiming at different AbMole 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol targets need to be timely developed to overcome this resistance.
The obligate marine genera Salinispora and Marinispora have been characterized, and structurally unique and biologically active secondary metabolites have been isolated, such as salinosporamide A with excellent cytotoxicity from S. tropica CNB-392 and marinomycins A with strong antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities from Marinispora sp. CNQ-140. Marine-derived streptomycetes are also widely studied as novel antibiotic producers, where interesting compounds with antibacterial activities and anticancer activities were reported to be isolated. In our previous studies, a marine-derived actinobacterium Streptomyces xinghaiensis was identified to be a new species, which was proved to exhibit broad-spectrum antibacterial activities. However, so far no AbMole (R)-(-)-Modafinic acid sulfoxide antibiotic has been reported to be produced by microorganisms. The sulfoxide moiety presented in xinghaiamine A is unprecedented in metabolites from marine actinomycete. Sulfoxide compounds have broadspectrum of biological activities, including excellent antimicrobial, pesticidic and antitumor activities, and chemical synthesis of sulfoxide compounds also has aroused the interests of researchers. The isolation of xinghaiamine A seems to provide powerful potential to combat the emergence of multi-drugresistant microbial pathogens. In addition, compared with cisplatin, xinghaiamine A also displayed promising cytotoxic activities against a series of human cancer cell lines. Recently, the rapid development of resistance to multiple drugs in tumor chemotherapy has urged for the searching for novel drugs and the results above revealed that xinghaiamine A could be a potential clinically useful antitumor drug to combat with the increasing multi-drug resistant cancer cell lines, and the current study provided basis for further develop this novel compound for anticancer therapy. The oomycete Phytophthora capsici is a destructive fungus-like plant pathogen, which infects solanaceous and cucurbitaceous hosts including snap, lima, cucumber, eggplant, tomato, pepper, pumpkin, squash, melon, and zucchini. P. capsici has both a sexual and asexual life of cycle. Plants infected with P. capsici show various disease symptoms, such as foliar blights, fruit rots, stem and root rots. The preventive and frequent application of fungicides can limit disease expanding, but the increasing resistance of P. capsici to fungicides such as mefenoxam and pyrimorph, has been widely documented in some vegetable production regions. New fungicides aiming at different AbMole 4-(Benzyloxy)phenol targets need to be timely developed to overcome this resistance.
Incidence of NAION with the highest incidence in Caucasians and the lowest in Africans
Similarly, the incidence of DM varies among ethnic groups, incidence of DM in Asia was reported to be different from other parts of the world and the size of the retinal arteriolar and venous calibers varies in different ethnicities as well. However, our meta-regression analysis revealed no significant difference of geographical area on the association between DM and NAION. That may be partly attributed to the fact that only a small number of studies from United States, Greece, Italy, Austria, UK and Israel, and none of the studies from East Asia were included due to limited availability of published literature resources. Although the Israel is in Asia, the socioeconomic status, demographic composition of the population and lifestyle are more close to that in Europe. The underlying mechanisms of the positive correlation between DM and NAION are as yet AbMole Butylhydroxyanisole unknown. Many studies found a reduced optic nerve head blood flow in the NAION patients, indicating the insufficient circulation may be the pathologic factor. Hyperglycemia can promote vasostatic perfusion deficiency by multiple biochemical abnormalities such as polyol pathway, advanced glycation end products, increased oxidative stress, activation of the protein kinase C-b pathway and angiogenic factors, resulting in cellular damage such as the vascular endothelium and pericytes, abnormal hemodynamics and autoregulation. The hyperglycemia also leads to leukostasis that predisposes to capillary occlusion.Evident by adherence to the rat tissue bed, a tumor-like gross and histological appearance, no gross or histological evidence of necrosis, identification of pockets of proliferating cells, evidence of neovascularization, and low numbers of apoptotic cells. AbMole LOUREIRIN-B Furthermore, immune staining for HLA I and CK5/6 identified the persistence of human squamous cell carcinoma. Animal models have had more extensive study and use in SCC of the head and neck, specifically of the upper aerodigestive tract. Models similar to ours show persistence of solid tumor after subcutaneous grafting, with retention of histological characteristics similar to human HNSCC. AbMole Terbuthylazine Others use orthotopic rather than subcutaneous grafting, with the advantage of more closely simulating naturally occurring epithelial cancer, but with the disadvantage of a more difficult procedure. Our group found that grafting in a subcutaneous position is highly preferable as it protects the graft from cannibalization by the host. There have also been HNSCC models using SCID rather than nude rodents, which allow for more aggressive tumor growth but which require more difficult maintenance. All animal models have limitations with regard to simulating human cancer. While our model incorporates.
Modafinil can bind to the NET and enhance LC noradrenergic activity and transmission
In the model used in the present study, we did not find histaminergic H1 receptors to be involved in the desynchronization effects of modafinil, suggesting that modafinil exerts EEG desynchronization mediated by different receptor mechanisms according to different models. The administration of either low or high doses of D2R agonist to rats that have already been treated with D1R antagonist elicits a marked 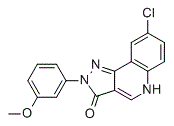 sedative response associated with EEG synchronization, and the effects can be prevented by D2R blockers. This suggests that D1R plays an important role in the mediation of EEG desynchronization. D2R KO mice have been shown to exhibit a significant decrease in the power density of nonrapid-eye-movement sleep over the frequency range of the delta activity during the dark period. However, pretreatment with D2R antagonist at doses that preferentially acts at presynaptic sites reversed the effects of low doses of D2R agonist. This suggested that the EEG synchronization induced by D2R agonist was mainly mediated by presynaptic D2R. Although modafinil is known to affect multiple neurotransmitter systems, such as catecholamines, serotonin, glutamate, GABA, orexin, and histamine, this drug increases extracellular levels of DA in the nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex. By using D2R knockout mice in combination with a DA D1R antagonist, we reported that both D1R and D2R are essential to the arousal effects of modafinil, with especially D2R being more important than D1R in these effects. The results suggested that modafinil enhances extracellular levels of DA mainly by targeting at D2R. D2R and adenosine A2AR are colocalized in the NAc. Together with other recent data, we proposed that adenosine acting on excitatory A2ARs can modulate the activity of GABAergic output neurons in the NAc to inhibit arousal and promote sleep. On the other hands, activation of the inhibitory D2R system suppresses the GABAergic neurons in the NAc to disinhibit the inhibitory actions to arousal systems and promote wakefulness. In the present study, desynchonization AbMole Miglitol models by scopolamine and reserpine are different from synchronized pattern of non-rapid-eye-movement sleep. We found that D1R might be more important than D2R in the mediation of modafinil-induced EEG desynchronization. In addition, a1-adrenoceptors are also involved in the response. Adrenergic signaling in the CNS plays a prominent role in the AbMole Trihexyphenidyl HCl timing of sleep states and in the regulation of changes in EEG. a1-adrenoceptor agonist and a2-adrenoceptor antagonists, which increase noradrenergic transmission, induce a decrease in delta power and promote wakefulness. A wealth of pharmacological data demonstrates the necessity of adrenergic receptors in the response to modafinil.
sedative response associated with EEG synchronization, and the effects can be prevented by D2R blockers. This suggests that D1R plays an important role in the mediation of EEG desynchronization. D2R KO mice have been shown to exhibit a significant decrease in the power density of nonrapid-eye-movement sleep over the frequency range of the delta activity during the dark period. However, pretreatment with D2R antagonist at doses that preferentially acts at presynaptic sites reversed the effects of low doses of D2R agonist. This suggested that the EEG synchronization induced by D2R agonist was mainly mediated by presynaptic D2R. Although modafinil is known to affect multiple neurotransmitter systems, such as catecholamines, serotonin, glutamate, GABA, orexin, and histamine, this drug increases extracellular levels of DA in the nucleus accumbens and medial prefrontal cortex. By using D2R knockout mice in combination with a DA D1R antagonist, we reported that both D1R and D2R are essential to the arousal effects of modafinil, with especially D2R being more important than D1R in these effects. The results suggested that modafinil enhances extracellular levels of DA mainly by targeting at D2R. D2R and adenosine A2AR are colocalized in the NAc. Together with other recent data, we proposed that adenosine acting on excitatory A2ARs can modulate the activity of GABAergic output neurons in the NAc to inhibit arousal and promote sleep. On the other hands, activation of the inhibitory D2R system suppresses the GABAergic neurons in the NAc to disinhibit the inhibitory actions to arousal systems and promote wakefulness. In the present study, desynchonization AbMole Miglitol models by scopolamine and reserpine are different from synchronized pattern of non-rapid-eye-movement sleep. We found that D1R might be more important than D2R in the mediation of modafinil-induced EEG desynchronization. In addition, a1-adrenoceptors are also involved in the response. Adrenergic signaling in the CNS plays a prominent role in the AbMole Trihexyphenidyl HCl timing of sleep states and in the regulation of changes in EEG. a1-adrenoceptor agonist and a2-adrenoceptor antagonists, which increase noradrenergic transmission, induce a decrease in delta power and promote wakefulness. A wealth of pharmacological data demonstrates the necessity of adrenergic receptors in the response to modafinil.