The economic impact of obesity on the United States was approximately $99.2 billion in 1995. The direct economic impact of obesity is similar to that of diabetes. Obese individuals report a high frequency of sexual difficulties often related to a reduced 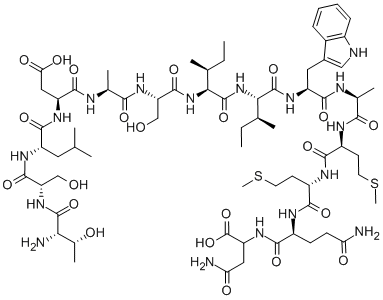 sexual drive and satisfaction, as well as a negative self-image. Non-surgical treatment has been ineffective in producing sustained weight loss among these individuals, and bariatric Oxysophocarpine surgery appears to be the most effective treatment for obesity, particularly among patients with a BMI.40 kg/m2 or those with a BMI.35 kg/m2 and significant obesity-related comorbidities. Dallal et al. reported that obesity-related sexual dysfunction could be reversible through gastric bypass surgery. However, the histologic and functional evaluations are as yet unknown. In 1954, an intestinal bypass operation as a potential treatment for obesity was first reported in a study using a dog model. Since then, many researchers have investigated mechanisms by which gastrointestinal bypass causes weight loss, and many have hypothesized malabsorption, caloric restriction, and gastric restriction to be the cause. However, none of these theories have provided sufficient explanation for clinical findings such as how the Roux-en-Y procedure can restore normal blood glucose levels in 84% of patients with obesity-related T2DM. Since this discovery, the relationship between bariatric surgery and glucose homeostasis has generated a tremendous research interest. Because the intestine itself produces, releases, and controls the endocrine signals of energy metabolism, gut hormones such as GLP-1, PYY, and ghrelin were considered responsible for weight loss and the restoration of glucose homeostasis following gastric bypass surgery. As with other theories, however, these theories based on gastrointestinal hormones remain Folic acid controversial. In our study, the cavernosal tissue in the control and bariatric surgery groups exhibited differences in biochemical and metabolic activities. In this T2DM rat model study, we have ascertained the effect of duodenojejunal bypass surgery on glucose homeostasis. These metabolic functional restorations are the key factors for micro-, macrostructural, and functional recovery. In the control group, the diminished glucose homeostasis led to structural and microvascular damage. The levels of eNOS and nNOS expression were diminished and Rho kinase expression was increased in the diabetic rats that had received the sham operation, compared to the rats that had received bariatric surgery. These resulted in cavernosal smooth muscle atrophy and vascular dysfunction. With these structural alterations, the functional result should be erectile dysfunction. However, in the bariatric surgery group we observed glucose homeostasis recovery that leads to metabolic and biochemical restoration, an increased level of eNOS, nNOS expression, and a diminished level of Rho kinase expression. This microvascular structural restoration leads to a macrostructural recovery, and thus, results in functional recovery. Reactive oxygen radicals are responsible for DNA damage, intracellular damage, apoptosis, and subsequently lead to endothelial fibrosis in the corpus cavernosum. 8-OHdG is an established indicator of DNA oxidative stress. In this study, the 8-OHdG level was lower in the rats that underwent bariatric surgery, indicating that bariatric surgery decreases oxidative stress associated with T2DM in the penile corpus cavernosum.
sexual drive and satisfaction, as well as a negative self-image. Non-surgical treatment has been ineffective in producing sustained weight loss among these individuals, and bariatric Oxysophocarpine surgery appears to be the most effective treatment for obesity, particularly among patients with a BMI.40 kg/m2 or those with a BMI.35 kg/m2 and significant obesity-related comorbidities. Dallal et al. reported that obesity-related sexual dysfunction could be reversible through gastric bypass surgery. However, the histologic and functional evaluations are as yet unknown. In 1954, an intestinal bypass operation as a potential treatment for obesity was first reported in a study using a dog model. Since then, many researchers have investigated mechanisms by which gastrointestinal bypass causes weight loss, and many have hypothesized malabsorption, caloric restriction, and gastric restriction to be the cause. However, none of these theories have provided sufficient explanation for clinical findings such as how the Roux-en-Y procedure can restore normal blood glucose levels in 84% of patients with obesity-related T2DM. Since this discovery, the relationship between bariatric surgery and glucose homeostasis has generated a tremendous research interest. Because the intestine itself produces, releases, and controls the endocrine signals of energy metabolism, gut hormones such as GLP-1, PYY, and ghrelin were considered responsible for weight loss and the restoration of glucose homeostasis following gastric bypass surgery. As with other theories, however, these theories based on gastrointestinal hormones remain Folic acid controversial. In our study, the cavernosal tissue in the control and bariatric surgery groups exhibited differences in biochemical and metabolic activities. In this T2DM rat model study, we have ascertained the effect of duodenojejunal bypass surgery on glucose homeostasis. These metabolic functional restorations are the key factors for micro-, macrostructural, and functional recovery. In the control group, the diminished glucose homeostasis led to structural and microvascular damage. The levels of eNOS and nNOS expression were diminished and Rho kinase expression was increased in the diabetic rats that had received the sham operation, compared to the rats that had received bariatric surgery. These resulted in cavernosal smooth muscle atrophy and vascular dysfunction. With these structural alterations, the functional result should be erectile dysfunction. However, in the bariatric surgery group we observed glucose homeostasis recovery that leads to metabolic and biochemical restoration, an increased level of eNOS, nNOS expression, and a diminished level of Rho kinase expression. This microvascular structural restoration leads to a macrostructural recovery, and thus, results in functional recovery. Reactive oxygen radicals are responsible for DNA damage, intracellular damage, apoptosis, and subsequently lead to endothelial fibrosis in the corpus cavernosum. 8-OHdG is an established indicator of DNA oxidative stress. In this study, the 8-OHdG level was lower in the rats that underwent bariatric surgery, indicating that bariatric surgery decreases oxidative stress associated with T2DM in the penile corpus cavernosum.
Author: targets inhibitor
In addition it is difficult to quantitatively manipulate population density at different
Most importantly, the rs6020 G-to-A polymorphism was highly prevalent in our Chinese population, but it is 0% in the Western population. The presence of the rs6020 G-to-A polymorphism predicted a high chance of coagulation Danshensu abnormalities in patients with ONFH. The marine bacterium Vibrio fischeri lives symbiotically in light organs of some fishes and squids, and exhibits bioluminescence at high population densities. Nealson et al. CAY10505 reported that this bioluminescence was due to the accumulation of an autoinducer, and that the intensity of bioluminescence positively correlated with bacterial population density. This phenomenon is called “quorum sensing”, and considerable attention has been paid to determine the signaling molecules involved in it. N-3oxohexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone, a type of acyl-homoserine lactone, was the first identified molecule in the process. Interestingly, AHL was found to freely diffuse through cell membranes and to play a role in cell�Ccell communication. As reported, at low bacterial population density, the concentration of AHLs remains low; however, their concentration increases with an increase in bacterial population density. At or above a particular threshold, they effectively bind to LuxR, which has been identified as an intracellular regulatory protein that mediates the formation of the LuxR:AHL complex. This dimer complex subsequently binds to the promoter of lux box and induces the expression of downstream genes such as luxC, luxD, luxA, luxB and luxE, which generates bioluminescence. V. fischeri lux box contains the promoters lux pL and lux pR that  regulate the transcription of luxR and luxI, respectively. luxI encodes a synthase, LuxI, which produces signaling molecule AHLs. luxI expression is upregulated by the interaction between the LuxR:AHL complex and lux box. Therefore, a positive feedback is involved in sensing signals. In brief, quorum sensing in bacterial bioluminescence is tightly controlled by several key elements such as lux box, luxR, and luxI. This provides the basis for building an artificial quorum-sensing circuit. You et al. reported a programmed cell-death circuit by cloning luxR and luxI under the control of a synthetic promoter Plac/ara-1, and cotransforming the bacterial lethal gene ccdB into Escherichia coli cells. These engineered bacteria could successfully produce and release autoinducer AHLs, which mediated luxR and ccdB expression in a feedback manner. As these engineered bacteria grew, they continuously released autoinducer AHLs into their environment. When AHL concentration reached a particular threshold, AHLs combined with LuxR and activated ccdB expression to produce CcdB. Consequently, CcdB poisoned bacterial gyrase and resulted in the death of numerous bacterial cells. However, when bacterial population density decreased, the concentration of LuxR:AHL dimer complexes required to activate lux pR was insufficient, and resulted in termination of cell death. Thereafter, the cells entered into a new round of growth. Once population density reached the abovementioned threshold, another round of cell death was triggered. This system successfully mimicked the situation of quorum sensing, in which bacterial cell growth and death could be regulated through bacterial population density. However, this system was cotransformed using two separate plasmids under the control the promoters Plac/ara-1 and PluxI. This could be problematic because of an imbalance in the copy numbers of the two plasmids, making it difficult to accurately investigate cellular communication on a genetic basis.
regulate the transcription of luxR and luxI, respectively. luxI encodes a synthase, LuxI, which produces signaling molecule AHLs. luxI expression is upregulated by the interaction between the LuxR:AHL complex and lux box. Therefore, a positive feedback is involved in sensing signals. In brief, quorum sensing in bacterial bioluminescence is tightly controlled by several key elements such as lux box, luxR, and luxI. This provides the basis for building an artificial quorum-sensing circuit. You et al. reported a programmed cell-death circuit by cloning luxR and luxI under the control of a synthetic promoter Plac/ara-1, and cotransforming the bacterial lethal gene ccdB into Escherichia coli cells. These engineered bacteria could successfully produce and release autoinducer AHLs, which mediated luxR and ccdB expression in a feedback manner. As these engineered bacteria grew, they continuously released autoinducer AHLs into their environment. When AHL concentration reached a particular threshold, AHLs combined with LuxR and activated ccdB expression to produce CcdB. Consequently, CcdB poisoned bacterial gyrase and resulted in the death of numerous bacterial cells. However, when bacterial population density decreased, the concentration of LuxR:AHL dimer complexes required to activate lux pR was insufficient, and resulted in termination of cell death. Thereafter, the cells entered into a new round of growth. Once population density reached the abovementioned threshold, another round of cell death was triggered. This system successfully mimicked the situation of quorum sensing, in which bacterial cell growth and death could be regulated through bacterial population density. However, this system was cotransformed using two separate plasmids under the control the promoters Plac/ara-1 and PluxI. This could be problematic because of an imbalance in the copy numbers of the two plasmids, making it difficult to accurately investigate cellular communication on a genetic basis.
Simple approaches such as restriction fragment length polymorphismbased assay
A negative regulator of ENaC in mouse endometrial epithelium which is important for liquid microenvironment during periimplantation. The abnormal expression of CFTR and  ENaCa might disrupt the cellular microenvironment that is harmful for embryo implantation or maintain of pregnancy; or might result from degeneration or necrosis of decidua as a consequence of miscarriage. Benzoylaconine However, the up-regulation of CFTR and downregulation of ENaC-a in mechanism of miscarriage remains unclear. CFTR and ENaC-a are ion channels that are co-expressed in a variety of cell types, including human endometrial and mouse endometrial cells. A previous study conducted in mice during preimplantation suggested that the CFTR protein was predominantly found in stromal cells, but not in epithelial cells, while the ENaC protein was predominantly localized to both luminal and glandular epithelial cells. Interestingly, in our study, we observed that the location of CFTR and ENaC-a protein expression in mouse uteri was not the same as that in human uteri. There are several reasons that might lead to these inconsistencies. Firstly, polyclonal antibodies used in the study might result in Diacerein non-specific expression; Secondly, the human decidua samples were obtained from cases of missed abortion and not fresh inevitable abortion; therefore, the tissue morphology might have been abnormal and luminal epithelia may not have been present. The exact mechanism associated with the spontaneous abortion in this model is unclear, and most studies have focused on abnormal immune reactions at the maternal-fetal interface. Several studies have demonstrated the predominance of Th2-type cytokines over Th1-type cytokines at the maternal-fetal interface in cases of successful pregnancy. However, in the CBA6DBA/2 model, increased expression of Th1-type cytokines such as interleukin -1, interferon -c, and tumor necrosis factor -a, and decreased expression of Th2-type cytokines such as transforming growth factor -b2, IL-4, and IL-10 are responsible for the spontaneous abortion. Interestingly, significantly higher IL-1b levels were found in the uterine fluid from women with repeated pregnancy failure after in vitro fertilization/embryo transfer. The interaction between ion channel and Th1-type cytokines is unclear. Some studies on respiratory and gastrointestinal system have suggested that IL-1b specifically upregulated CFTR gene expression in human intestinal T84 cells. The most frequently reported techniques used for DNMT3A mutations include direct sequencing, high-resolution melting analysis and next generation sequencing. Sanger sequencing is particularly well-established techniquefor the identification of previously unreported mutations but its relatively low sensitivitymay be problematic for detection of low frequency somatic mutations. High resolution meltingtechnique has also been adapted for detection of DNMT3A mutations and is also good for screening for unknown mutations in a single tube format with a sensitivity of about 4%. However, it requires well-established standards and eventually verification of the result through direct sequencing. Targeted amplicon resequencing on next generation sequencingplatforms has also been used for DNMT3A mutations. The obvious advantages of NGS as the digital allele burden output, theoretically very high sensitivity, the possibility for identification of novel mutations are currently limited by the costly equipment and the necessity for a strong bioinformatic support.
ENaCa might disrupt the cellular microenvironment that is harmful for embryo implantation or maintain of pregnancy; or might result from degeneration or necrosis of decidua as a consequence of miscarriage. Benzoylaconine However, the up-regulation of CFTR and downregulation of ENaC-a in mechanism of miscarriage remains unclear. CFTR and ENaC-a are ion channels that are co-expressed in a variety of cell types, including human endometrial and mouse endometrial cells. A previous study conducted in mice during preimplantation suggested that the CFTR protein was predominantly found in stromal cells, but not in epithelial cells, while the ENaC protein was predominantly localized to both luminal and glandular epithelial cells. Interestingly, in our study, we observed that the location of CFTR and ENaC-a protein expression in mouse uteri was not the same as that in human uteri. There are several reasons that might lead to these inconsistencies. Firstly, polyclonal antibodies used in the study might result in Diacerein non-specific expression; Secondly, the human decidua samples were obtained from cases of missed abortion and not fresh inevitable abortion; therefore, the tissue morphology might have been abnormal and luminal epithelia may not have been present. The exact mechanism associated with the spontaneous abortion in this model is unclear, and most studies have focused on abnormal immune reactions at the maternal-fetal interface. Several studies have demonstrated the predominance of Th2-type cytokines over Th1-type cytokines at the maternal-fetal interface in cases of successful pregnancy. However, in the CBA6DBA/2 model, increased expression of Th1-type cytokines such as interleukin -1, interferon -c, and tumor necrosis factor -a, and decreased expression of Th2-type cytokines such as transforming growth factor -b2, IL-4, and IL-10 are responsible for the spontaneous abortion. Interestingly, significantly higher IL-1b levels were found in the uterine fluid from women with repeated pregnancy failure after in vitro fertilization/embryo transfer. The interaction between ion channel and Th1-type cytokines is unclear. Some studies on respiratory and gastrointestinal system have suggested that IL-1b specifically upregulated CFTR gene expression in human intestinal T84 cells. The most frequently reported techniques used for DNMT3A mutations include direct sequencing, high-resolution melting analysis and next generation sequencing. Sanger sequencing is particularly well-established techniquefor the identification of previously unreported mutations but its relatively low sensitivitymay be problematic for detection of low frequency somatic mutations. High resolution meltingtechnique has also been adapted for detection of DNMT3A mutations and is also good for screening for unknown mutations in a single tube format with a sensitivity of about 4%. However, it requires well-established standards and eventually verification of the result through direct sequencing. Targeted amplicon resequencing on next generation sequencingplatforms has also been used for DNMT3A mutations. The obvious advantages of NGS as the digital allele burden output, theoretically very high sensitivity, the possibility for identification of novel mutations are currently limited by the costly equipment and the necessity for a strong bioinformatic support.
Structural information is available for any protein component of the MtrCDE tripartite complex system
To elucidate the mechanism used by this efflux system for multidrug recognition and extrusion, we here describe the crystal Miglitol structure of the inner membrane MtrD multidrug efflux pump. The findings reveal a novel structural feature that is not found in other known RND efflux pumps. Natural productshave been the major sources for clinical drug discovery and development for many decades. NPs with novel activities or skeletons are constantly needed to antagonize newly emerging threats to human health. In recent years, the explosion of genome sequencing has led to rapid development of novel NP screening approaches which have greatly increased the number and diversity of NPs inventories. As a correlation to this increase, understanding how the NPs are biosynthesized is also very important. Accessing to the mechanisms underlying NPs biosynthesis will not only improve our knowledge of various kinds of enzymatic reactions, but also pave the ways for future combinatorial biosynthesis which can guide medicinal chemistry in developing more applicable NP-derived drugs. Adequate structural information of biosynthesis intermediates or analogs is generally required to establish an unambiguous biosynthetic pathway for a particular NP. However, due to the low concentrations or insignificant bio-activities of individual candidates or insufficient speculation on the candidates’ structures, potential intermediates and analogs accumulated in the fermentation culture of the producing strain were often overlooked in liquid chromatographyand mass spectrometryanalysis.Therefore, the progress toward revealing the NPs’ biosynthetic  mechanisms has significantly lagged behind those toward NP discovery and screening, thus prompting the need for effective solutions. Pyrrolamides, biosynthesized by Streptomyces and related actinobacteria, are a class of poly-pyrrolic natural products containing one or more pyrrole-2-carboxamide moieties in their structures. Most pyrrolamides, including congocidine, distamycin, and pyrronamycin B, are found to possess the ability to bind to specific DNA sequences, which enables this compound group with many desirable biological activities. Although the discovered natural pyrrolamides are still too toxic for clinical use, these molecules are still attractive in the field of pharmacology because their selective DNA sequence binding features may inspire the development of special drugs. Additionally, numerous efforts have been made to Gentamycin Sulfate chemically synthesize several DNA-binding agents based on pyrrolamide structures. Thus, exploring novel NPs belonging to the pyrrolamide family can provide more skeleton hints to current DNA-binding pharmaceutical research. Recently, the first pyrrolamide gene cluster directing congocidine biosynthesis is identified in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Juguet et al. demonstrated that congocidine is assembled by an iterative nonribosomal peptide synthetase. In another work, nearly every gene in the congocidine gene cluster is separately inactivated, and LCMS analysis of the related mutants showed that 4-acetamidopyrrole-2-carboxylate is the key precursor for pyrrolamide biosynthesis. However, the main mechanism underlying the control of pyrrole polymerization, which may be the most intriguing question in oligo-pyrroles NP biosynthesis.
mechanisms has significantly lagged behind those toward NP discovery and screening, thus prompting the need for effective solutions. Pyrrolamides, biosynthesized by Streptomyces and related actinobacteria, are a class of poly-pyrrolic natural products containing one or more pyrrole-2-carboxamide moieties in their structures. Most pyrrolamides, including congocidine, distamycin, and pyrronamycin B, are found to possess the ability to bind to specific DNA sequences, which enables this compound group with many desirable biological activities. Although the discovered natural pyrrolamides are still too toxic for clinical use, these molecules are still attractive in the field of pharmacology because their selective DNA sequence binding features may inspire the development of special drugs. Additionally, numerous efforts have been made to Gentamycin Sulfate chemically synthesize several DNA-binding agents based on pyrrolamide structures. Thus, exploring novel NPs belonging to the pyrrolamide family can provide more skeleton hints to current DNA-binding pharmaceutical research. Recently, the first pyrrolamide gene cluster directing congocidine biosynthesis is identified in Streptomyces ambofaciens. Juguet et al. demonstrated that congocidine is assembled by an iterative nonribosomal peptide synthetase. In another work, nearly every gene in the congocidine gene cluster is separately inactivated, and LCMS analysis of the related mutants showed that 4-acetamidopyrrole-2-carboxylate is the key precursor for pyrrolamide biosynthesis. However, the main mechanism underlying the control of pyrrole polymerization, which may be the most intriguing question in oligo-pyrroles NP biosynthesis.
More over they suggest that 6MWT is a potential alternative to treadmill exercise testing for assessment of prognosis
In addition, Beatty et.al.revealed that the 6MWTD can predicts MACE in a broader population of patients with stable CHD, independent of traditional risk factors and markers of cardiac disease severity. Treadmill exercise testing will remain the preferred modality for evaluating patients with suspected ischemia. Amikacin hydrate However, for STEMI patients undergoing risk stratification for further intervention, the 6MWT offers potential advantages. The 6MWT can be conducted with little equipment other than a hallway marked for distance and a stopwatch. Due to the self-paced nature of the test, side effects of chest pain, dyspnea, or musculoskeletal pain are usually mild; serious adverse events have not been described. Further, the 6MWT is less expensive than treadmill exercise testing. The ability of the 6MWT, a simple office-based test of functional exercise capacity, to predict outcomes in patients with stable CHD is especially relevant because the 6MWT addresses physical activity, a modifiable risk factor for secondary prevention of CHD. While we  have demonstrated in the present work that the 6MWTD can predict cardiovascular events in STEMI patients, however, its use for improving prognosis merits further study. The use of Treadmill exercise stress test as a control group was not valid in this study however, we recommend adding it in future studies. We cannot exclude the possibility of selection bias in the main cohort of participants, since many CCU admitted patients were not enrolled in the study for logistical reasons. Patients were excluded from the study if they were unable to walk. Thus, the results may not extend to patients with significant angina or other limitations in walking. The transcripts of lncRNAs contain more than 200 nucleotides and have little or no potential translation. Although once thought to have no function, the expression of these novel RNAs have been shown to be cell type-specific, localized to sub-cellular compartments, and associated with diverse human diseases including a number of cancers. Correlations between lncRNA expression and cancer has attracted worldwide research attention, as well the reported functions of lncRNAs in gene expression regulation, splicing, epigenetic control, chromatin structure, and nuclear transport. Such correlations may be positive or negative. For example, the well-known lncRNA Hox antisense intergenic RNAis a powerful predictor of metastasis and poor prognosis, and is overexpressed in breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinomaand colorectal cancer, to name a few. Conversely, the lncRNA maternally expressed gene 3is downregulated in HCC, and enforced expression of MEG3 in HCC cells significantly decreased both anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent cell growth, and induced apoptosis. Renal cell carcinomais one of the most Ascomycin common malignant cancers in China. It was estimated that 37.7 men and 16.6 women per 100,000 Chinese were diagnosed with RCC in 2005. The disease is the third most common genitourinary cancer, and for the year 2008 in the United States 54,390 casesand 13,010 deaths were expected. Although in most patients RCC is primary, up to 40% will eventually develop metastases. Patients with metastatic RCC have a median survival of only 6�C12 months and only 9% survive 5 years, largely because of strong resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy and the lack of effective therapeutics.
have demonstrated in the present work that the 6MWTD can predict cardiovascular events in STEMI patients, however, its use for improving prognosis merits further study. The use of Treadmill exercise stress test as a control group was not valid in this study however, we recommend adding it in future studies. We cannot exclude the possibility of selection bias in the main cohort of participants, since many CCU admitted patients were not enrolled in the study for logistical reasons. Patients were excluded from the study if they were unable to walk. Thus, the results may not extend to patients with significant angina or other limitations in walking. The transcripts of lncRNAs contain more than 200 nucleotides and have little or no potential translation. Although once thought to have no function, the expression of these novel RNAs have been shown to be cell type-specific, localized to sub-cellular compartments, and associated with diverse human diseases including a number of cancers. Correlations between lncRNA expression and cancer has attracted worldwide research attention, as well the reported functions of lncRNAs in gene expression regulation, splicing, epigenetic control, chromatin structure, and nuclear transport. Such correlations may be positive or negative. For example, the well-known lncRNA Hox antisense intergenic RNAis a powerful predictor of metastasis and poor prognosis, and is overexpressed in breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinomaand colorectal cancer, to name a few. Conversely, the lncRNA maternally expressed gene 3is downregulated in HCC, and enforced expression of MEG3 in HCC cells significantly decreased both anchorage-dependent and anchorage-independent cell growth, and induced apoptosis. Renal cell carcinomais one of the most Ascomycin common malignant cancers in China. It was estimated that 37.7 men and 16.6 women per 100,000 Chinese were diagnosed with RCC in 2005. The disease is the third most common genitourinary cancer, and for the year 2008 in the United States 54,390 casesand 13,010 deaths were expected. Although in most patients RCC is primary, up to 40% will eventually develop metastases. Patients with metastatic RCC have a median survival of only 6�C12 months and only 9% survive 5 years, largely because of strong resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy and the lack of effective therapeutics.