Its capacity to do so makes the method a powerful tool for answering emerging questions about the role of B-cells in regulating auto-immunity, and able to clarify the divergent behaviors of B-cell subpopulations. It may furthermore strengthen existing strategies for monoclonal antibody therapy development, by linking sets of 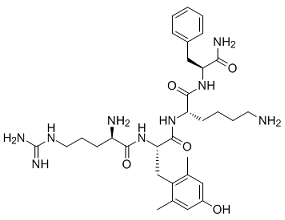 antibody mutations with the up- and down-regulation of genes associated with antigen-binding. Taken together, our results demonstrate the power of this simultaneous gene-expression and mutation measurement to elucidate statistical relationships and heterogeneity otherwise hidden from studies that treat such cellpopulations in bulk. Congenital hypothyroidism is one of the most common preventable causes of mental retardation. Neonatal screening programs allow for the early detection and treatment of CH, thus preventing the mental retardation that results from the lack of thyroid hormone. Despite the unquestioned public health success of newborn screening programs and management of CH, there are still gaps in knowledge. For example, one important challenge in understanding the epidemiology of CH is that some newborns will have transient CH, a temporary depression of thyroid hormone concentrations that can last from several days to several months. Transient congenital hypothyroidism reverts later to normal, which may or may not require replacement therapy. Its incidence varies depending on whether the condition is defined on the basis of abnormal neonatal screening tests for congenital hypothyroidism alone or whether the diagnosis is considered only if the abnormality persists in the confirmatory tests. Permanent dysfunction mainly results from maldevelopment, absence or ectopic thyroid gland, whereas the underlying causes of transient functional impairment are less clear and may include maternal factors such as iodine deficiency, excessive iodine intake, anti-thyroid medication or presence of antibodies against thyroid tissue during pregnancy. Also neonatal very low birth weight and prematurity, immaturity of thyroidal iodine organification, exposure to excess iodine and gene mutation may contribute to transient CH. Diagnosis of transient hypothyroidism is important to avoid lifelong unnecessary therapy with its possible side effects. Besides, the governmental financial burden for this unnecessary therapy could be invested in other purposive health services. Iodine deficiency is a global health problem. Goiter has been known to exist in Egypt since Ancient times, Papyrus dating since 1500 BC reported thyroidectomy and there are suggestions that Cleopatra had goiter. The UNICEF categorized Egypt as one of the countries with low iodinated salt consumption with large number of neonates exposed to iodine deficiency. Moreover our governorate, being an oasis is one of the areas that are highly affected by iodine deficiency in soil and food sources.
antibody mutations with the up- and down-regulation of genes associated with antigen-binding. Taken together, our results demonstrate the power of this simultaneous gene-expression and mutation measurement to elucidate statistical relationships and heterogeneity otherwise hidden from studies that treat such cellpopulations in bulk. Congenital hypothyroidism is one of the most common preventable causes of mental retardation. Neonatal screening programs allow for the early detection and treatment of CH, thus preventing the mental retardation that results from the lack of thyroid hormone. Despite the unquestioned public health success of newborn screening programs and management of CH, there are still gaps in knowledge. For example, one important challenge in understanding the epidemiology of CH is that some newborns will have transient CH, a temporary depression of thyroid hormone concentrations that can last from several days to several months. Transient congenital hypothyroidism reverts later to normal, which may or may not require replacement therapy. Its incidence varies depending on whether the condition is defined on the basis of abnormal neonatal screening tests for congenital hypothyroidism alone or whether the diagnosis is considered only if the abnormality persists in the confirmatory tests. Permanent dysfunction mainly results from maldevelopment, absence or ectopic thyroid gland, whereas the underlying causes of transient functional impairment are less clear and may include maternal factors such as iodine deficiency, excessive iodine intake, anti-thyroid medication or presence of antibodies against thyroid tissue during pregnancy. Also neonatal very low birth weight and prematurity, immaturity of thyroidal iodine organification, exposure to excess iodine and gene mutation may contribute to transient CH. Diagnosis of transient hypothyroidism is important to avoid lifelong unnecessary therapy with its possible side effects. Besides, the governmental financial burden for this unnecessary therapy could be invested in other purposive health services. Iodine deficiency is a global health problem. Goiter has been known to exist in Egypt since Ancient times, Papyrus dating since 1500 BC reported thyroidectomy and there are suggestions that Cleopatra had goiter. The UNICEF categorized Egypt as one of the countries with low iodinated salt consumption with large number of neonates exposed to iodine deficiency. Moreover our governorate, being an oasis is one of the areas that are highly affected by iodine deficiency in soil and food sources.